 The National River Flow Archive (NRFA) is the UK's focal point for river flow data. The NRFA collates, quality controls, and archives hydrometric data from gauging station networks across the UK maintained by the Environment Agency, Natural Resources Wales, Scottish Environment Protection Agency and Department for Infrastructure - Rivers. There are over 1,600 gauging stations equating to 22 million flow values. The longest records stretch back to the late 19th Century. Our river flow data are used to underpin much of the hydrological research and water resources development and management activity in the UK.
The National River Flow Archive (NRFA) is the UK's focal point for river flow data. The NRFA collates, quality controls, and archives hydrometric data from gauging station networks across the UK maintained by the Environment Agency, Natural Resources Wales, Scottish Environment Protection Agency and Department for Infrastructure - Rivers. There are over 1,600 gauging stations equating to 22 million flow values. The longest records stretch back to the late 19th Century. Our river flow data are used to underpin much of the hydrological research and water resources development and management activity in the UK.
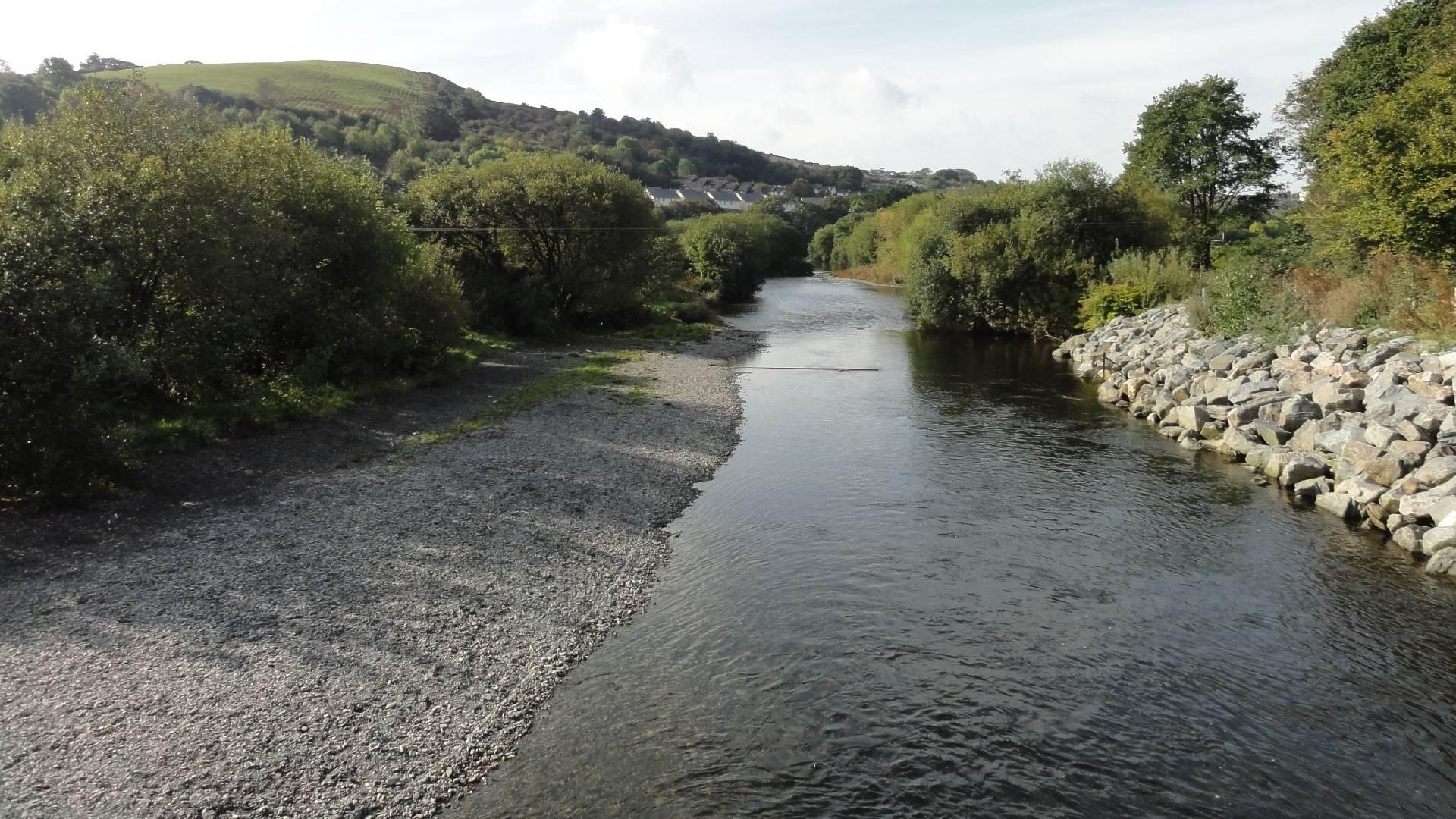
The NRFA holds daily mean flow data, peak flow data and catchment average rainfall data, alongside a wealth of metadata, spatial information and photographs all gathered together in one place to provide context to the community when using the data.
These portals are intended to be companion products.

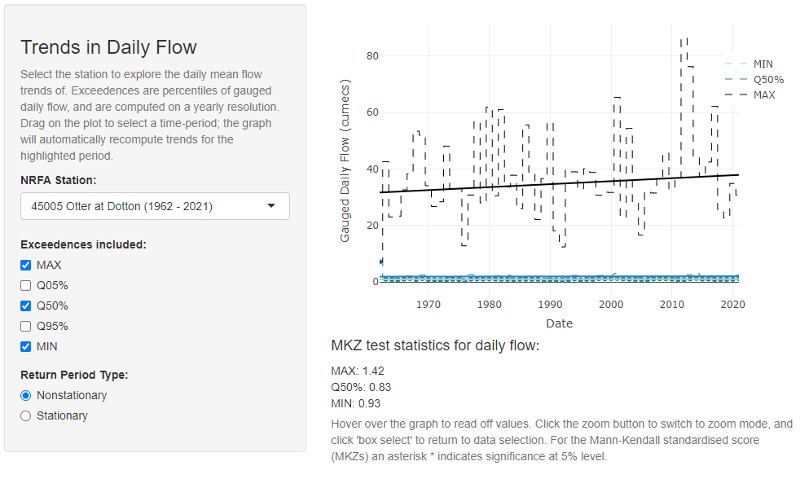 The UK Benchmark Network (UKBN) comprises a subset of gauging stations from the national hydrometric network that are most suited for identification and interpretation of long-term hydrological variability and change. Benchmark catchments can be considered reasonably free from human disturbances such as urbanisation, river engineering, and water abstractions, so are 'near-natural' and hence can be used for detection of climate-driven changes in river flow. These stations are available in the
The UK Benchmark Network (UKBN) comprises a subset of gauging stations from the national hydrometric network that are most suited for identification and interpretation of long-term hydrological variability and change. Benchmark catchments can be considered reasonably free from human disturbances such as urbanisation, river engineering, and water abstractions, so are 'near-natural' and hence can be used for detection of climate-driven changes in river flow. These stations are available in the 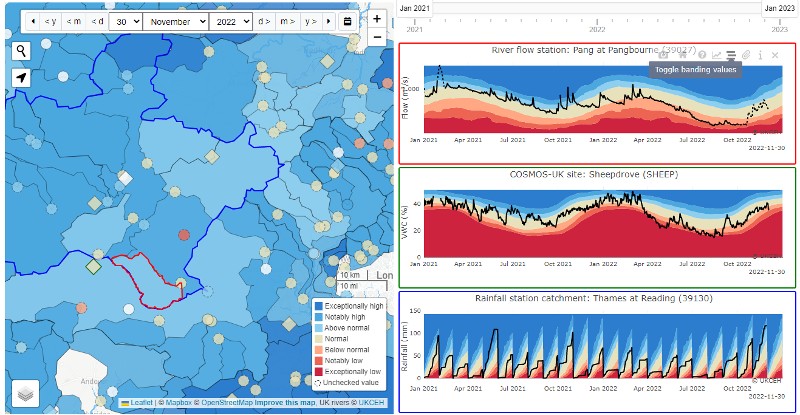 The
The 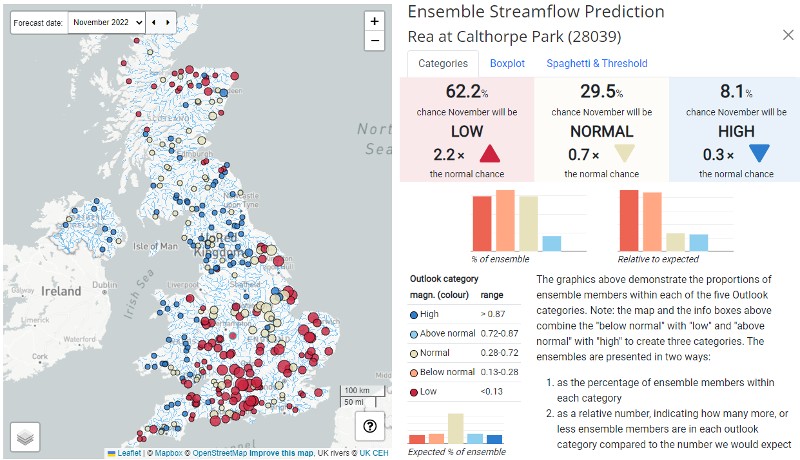 The
The 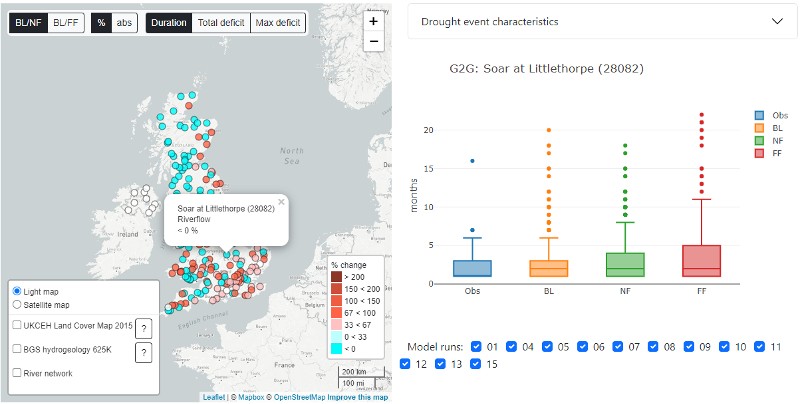 The Enhanced Future Flows and Groundwater (eFLaG) dataset is a set of nationally consistent climatological and hydrological projections based on UKCP18 that can be used by the water industry for water resources and drought planning amongst many other uses. The
The Enhanced Future Flows and Groundwater (eFLaG) dataset is a set of nationally consistent climatological and hydrological projections based on UKCP18 that can be used by the water industry for water resources and drought planning amongst many other uses. The